Recent Talks
List of all the talks in the archive, sorted by date.

Abstract
El presente trabajo analiza cómo es el proceso de gestión del conocimiento científico en el Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) como caso paradigmático de un entorno de coopetición donde se coopera y se compite en aras de lograr la excelencia científica. Para ello se ha llevado a cabo un estudio cualitativo y cuantitativo del Área de Investigación del IAC, que ha permitido tener una visión de los diferentes aspectos que determinan dicho proceso (capital humano, social y organizativo; capacidades directivas y prácticas de RRHH). Además de evidenciar los principales hallazgos sobre el bienestar laboral de los investigadores, también se analizarán los resultados alcanzados desde la perspectiva de género. Finalmente, se presentarán las conclusiones y recomendaciones del estudio.

Abstract

Abstract
The Institute for Astrophysics and Geophysics (IAG) in Göttingen operates a Fourier-Transform Spectrograph (FTS) that can be fed by either a 50cm siderostat or an integrating sphere. In 2016, we published a solar flux atlas (disk-integrated) at wavelengths 405-2300nm. Being largely comparable to the Kitt Peak spectral atlases in terms of resolution and signal-to-noise, our focus lies on an accurate calibration of frequencies (wavelengths) because we are interested in absolute convective blueshift of solar surface features.
Recently, we published an atlas of the quiet solar surface at different limb positions (spatially resolved Sun) and investigated convective velocities across the solar surface and in different spectral lines (Ellwarth et al., 2023 and in press). Furthermore, we studied the impact of centre-to-limb variation on exoplanet transit observations (Reiners et al., 2023). We are currently collecting data of active solar regions with the goal to measure convective blueshift as a function of limb position and magnetic field strength. In the talk, I will provide an overview of our program with a focus on the challenges we met in our attempts to determine Doppler velocities at the solar surface at m/s accuracy.
Zoom link: https://rediris.zoom.us/j/97531318437?pwd=TEpGZGVkNkpBcXBLWVlNTGt6bkdNUT09
Meeting ID: 975 3131 8437
Passcode: 147922

Abstract
Using unsupervised machine learning methods, we present a novel approach to classifying galaxies into early and late types based on their spectral characteristics. The research utilizes a balanced dataset of 2000 galaxies from the Galaxy Zoo 2 and spectral data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 13. The methodology involves applying an Autoencoder Neural Network for dimensionality reduction, followed by a Gaussian Mixture Model for clustering. The study demonstrates that this approach achieves an accuracy rate of approximately 86% in galaxy classification, highlighting the potential of unsupervised machine learning techniques in enhancing the precision and efficiency of morphological classification of galaxies based on spectral data.
Abstract
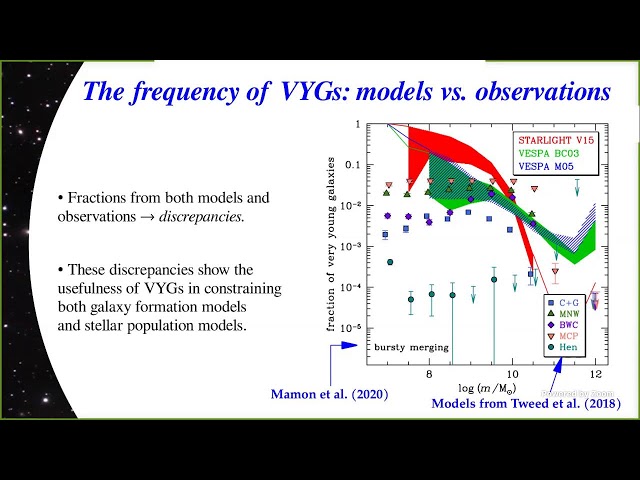
In the local Universe, there are a handful of dwarf star-forming galaxies that are young, having formed a large fraction of their stellar mass during their last few hundred Myr. However, little is known about the fraction of young stellar populations in more massive galaxies. Using the data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, we identified a surprisingly large sample of more massive, very young galaxies (VYGs), defined to have formed at least 50 per cent of their stellar mass within the last 1 Gyr. In this seminar, I will present our study on the fractions, properties and environment of low-redshift VYGs in observations and simulations, discuss possible mechanisms responsible for the recent triggering of intense star formation activity in these systems, and argue that VYGs can be useful in constraining the uncertainties in both galaxy formation models and spectral modelling of galaxy star formation histories.
Abstract
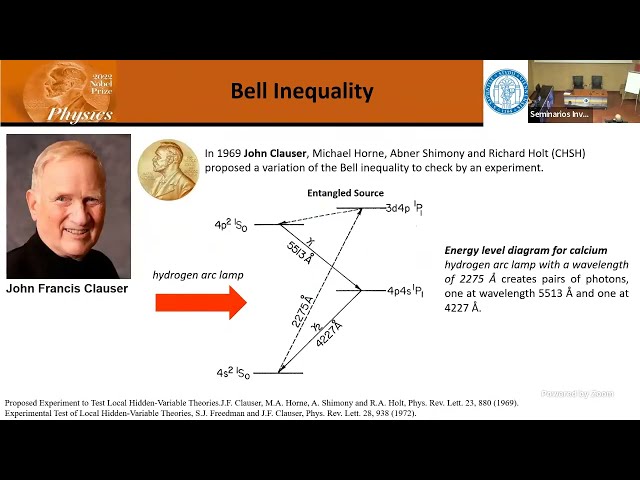
"God does not play dice.", this is the famous quoted by Einstein who believed that quantum mechanics is not complete and could not possibly explain everything about
nature. However, in 2022, John F. Clauser, Alain Aspect, and Anton Zeilinger were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for their groundbreaking experimental proof of
Bell's inequality, effectively demonstrating entanglement as a defining characteristic of quantum mechanics. However, some assumptions have been considered to experimentally
verify the Bell’s Inequality which is known as loopholes. One of which is the 'freedom of choice' loophole, questions the absence of statistical correlations between measurement
settings and external factors influencing the outcomes. In this presentation, I will delve into some work of Prof. Zeilinger's research group, which culminated in their prestigious
Nobel Prize and were performed at La Palma and Tenerife Islands. Moreover, I will talk on their recently pioneering use of distant astronomical sources as 'cosmic setting
generators'. This innovative approach allowed us to reach back in time, extending our understanding to approximately 7.8 billion years ago the most recent period beyond
which any local-realist influences could manipulate the 'freedom-of-choice' loophole and impact the observed Bell violations. Furthermore, the exciting prospects of identifying
potential sources that could extend this temporal boundary even further will be explored.

Abstract
El Telescopio Solar Europeo (EST) se construirá en el Observatorio del Roque de los Muchachos, un lugar conocido por sus excelentes condiciones de observación. El propio diseño de EST puede influir en estas condiciones y afectar a su calidad óptica en un efecto denominado ‘seeing’ local. La Oficina de Proyecto de EST ha implementado una nueva metodología para estimar el ‘seeing’ local combinando análisis térmicos, de dinámica de fluidos y ópticos. En esta presentación se expondrá esta metodología y su aplicación en criterios de diseño.
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h76KS893uY4
Abstract
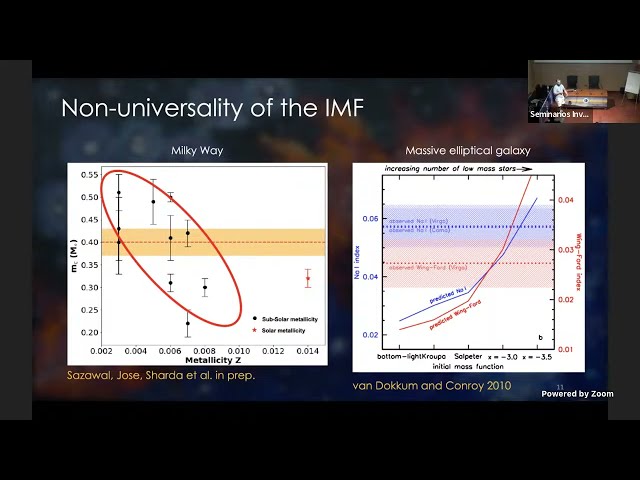
From the time the first stars formed to the present-day, metals have witnessed the assembly of structure in the Universe in great detail. Although metals only form in stars and stellar remnants, they are ubiquitously present everywhere. However, we still do not understand how metals are effectively dispersed throughout the Universe, and the various roles they play in shaping galaxies. In this talk, I will present a multi scale approach to study the role of metals in galaxy evolution, from molecular clouds to galactic discs. On smaller scales, I will focus on physical processes that shape up the initial mass function (IMF, with a particular emphasis on metal-free and metal-poor environments) that directly set the integrated yield of metals in the first and early galaxies. I will discuss results from high resolution radiation chemo-magnetohydrodynamic simulations that study the impact of turbulence, radiation feedback and magnetic fields on the primordial IMF, and describe analytical models of dusty molecular clouds that explain the transition in the IMF as the metal abundance grows over cosmic time. On larger scales, the talk will cover the physics of gas-phase metal distribution in galaxies. Using a combination of spatially-resolved gas-phase metallicity measurements and novel semi-analytical models, I will present recent results that advance our understanding of metallicity gradients in (late type) galaxies. In particular, I will show how self-consistently incorporating metal dynamics into galaxy evolution models is key to explaining the observed trends in metallicity gradients with galaxy mass, metallicity, and kinematics. I will end by highlighting how ongoing/upcoming astronomical facilities will transform our understanding of metal evolution in galaxies.

Abstract
Galaxies are embedded within a network of interconnected filaments, essential for their formation and growth. Simultaneously, they emit radiation and enriched matter back into their environment, influencing the evolution of the cosmic gas. Recent advancements in wide-field spectrographs offer a unique perspective, allowing us to probe the spatial distribution and properties of the circumgalactic medium at high redshift, particularly the Lyman-alpha line emitted by cold hydrogen gas. These insights are especially valuable in overdense regions, like protoclusters and groups, where we can explore most of the physical mechanisms at play. By combining data from instruments such as KCWI, MOSFIRE, IRAC, LRIS, and HST, we aim to decipher the various mechanisms that steer the evolution of galaxies and protocluster environments around the Cosmic Noon epoch, unveiling how mergers, AGN feedback, and galactic outflows influence both the large-scale gas distribution and the general properties of the galaxies themselves. Nonetheless, several degeneracies persist among the observed properties of the gas and the potential physical mechanisms responsible, underscoring the necessity for improved models of these cosmic phenomena and a larger statistical sample of protocluster environments.
Abstract
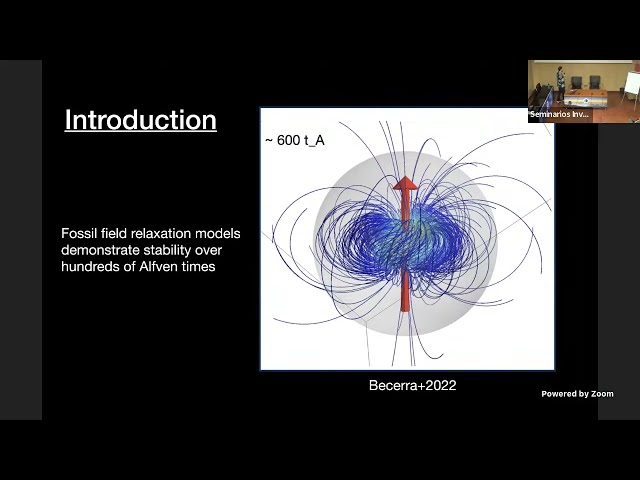
Magnetism is ubiquitous in the Universe, yet understanding the magnetic properties of stars continues to present intriguing challenges. Recent advancements owe their success to large-scale optical spectropolarimetric surveys, asteroseismic inferences, and new modelling methodologies. This presentation focuses on the evolution of massive stars with OB spectral types, with a particular emphasis on the incorporation of magnetic field effects into one-dimensional (1D) evolutionary model calculations. We explore the distinctiveness of these magnetic models in contrast to their non-magnetic counterparts, shedding light on the substantial influence of large-scale, organized magnetic fields on the physical characterization of stars. In particular, we investigate surface phenomena, such as mass loss and angular momentum loss, and their profound impact on the evolutionary trajectories of hot, massive stars. We will conclude by outlining future avenues to improve 1D models and addressing some of the remaining challenges in describing the magnetic characteristics of stars.
Upcoming talks
No talks scheduled for the next days.








