Found 6 talks width keyword galactic interactions

Abstract
Galaxies and the dark matter halos in which they reside are intrinsically connected. That relationship holds information about key processes in galaxy and structure formation. In this talk, I will consider how the galaxy-halo connection depends on position within the cosmic web - the familiar decomposition of large-scale structure in filaments, knots and voids. Simulations demonstrate the various ways in which the cosmic web modulates the growth and dynamics of halos. The extent to which the cosmic web impacts on galaxies is more difficult to establish. For example, galaxies might be sensitive only to the evolution of the host halo, in which case any effect of the cosmic web on galaxies is secondary, and can be inferred from the halo's history. There is evidence, however - from simulations and observations - that the cosmic web also impacts on the evolution of galaxies via the effect it has on the broader gas ecosystem in which they are embedded, as well as through "pre-processing" effects on group scale. So, how should we think of the cosmic web in its role as a transformative agent of galaxies? And what physical processes can we convincingly constrain from observations and simulations? In this talk I highlight recent work that addresses these questions.
Abstract
Youtube933518
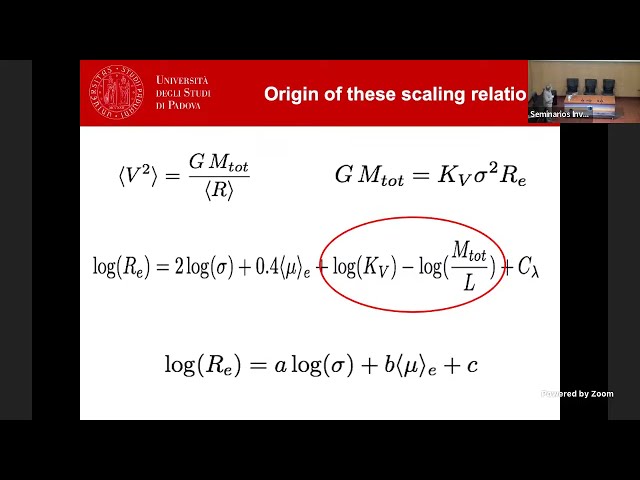
Abstract
I present a detailed analysis of the scaling relations of ETGs and suggest a way to predict the evolution of the distributions of galaxies in these planes. This new approach is able to account of several features observed in the FP projections and of the tilt of the Fundamental Plane.
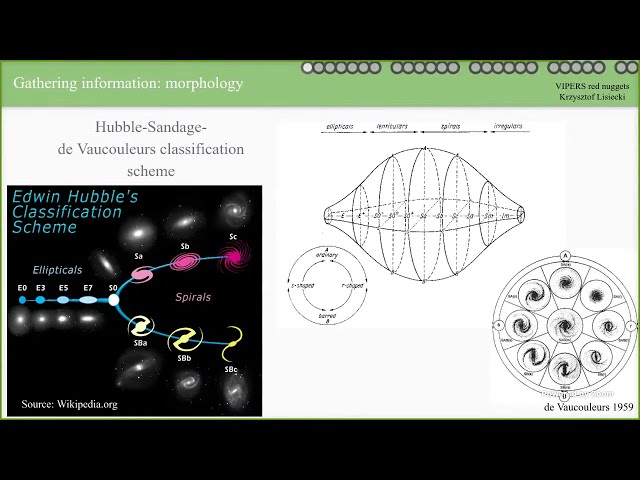
Abstract
Vimos Public Extragalactic Redshift Survey (VIPERS) is a spectroscopic survey designed to investigate the spatial distribution of ~90k galaxies on redshift 0.4<z<1.2. The catalogue of spectroscopic observations, combined with auxiliary photometric data, is perfect for evolutionary studies of different types of galaxies. But also for tracing rare objects. One of them are the so-called “red nuggets”, progenitors of the most massive galaxies in the local Universe. The discovery of red nuggets - highly massive, passive and extremely compact galaxies - at high redshift challenged the leading cosmological models, as they do not fit into the evolutionary paths of passive galaxies. Taking into account that the galaxies' mergers are stochastic events, it is possible that some red nuggets remain relatively unaltered for billions of years. Those survivors constitute a group of unique galaxies in the local Universe, commonly named “relics”. Despite numerous studies dedicated to red nuggets and relics, the link between the population of compact, massive, passive galaxies in the early Universe and their remnants in the local Universe, is still poorly understood.
In my talk I will present the first spectroscopically selected catalogue of red nuggets at the intermediate redshift. It is the most extensive catalogue of this kind of galaxies above redshift z > 0.5. Selected under the most strict criteria, the group of 77 objects consists of a statistically important sample, which allows for analysis of physical properties of those rare passive giants. I will discuss the influence of compactness criteria on the sample size. Moreover I will present VIPERS red nuggets number densities and discuss the environmental preferences of those exceptional galaxies.

Abstract
In the 50 years since their discovery, it has become increasingly recognised that quasars are not merely signposts to the distant Universe, but also play a key role in the overall galaxy evolution process. However, if we are to incorporate quasars into models of galaxy evolution, it's important to understand how, when and where they are triggered. In this talk I will review the latest observational results on the triggering of quasars, based on the morphologies of their host galaxies and star formation properties; I will also discuss the future prospects for understanding quasar triggering using Herschel and ALMA data.

Abstract
The mechanism by which AGN activity is triggered has long been debated. One, often suggested, method of doing so is major, gas-rich mergers and galaxy interactions. I will present deep Gemini GMOS-S images of a sample of type II quasar host galaxies, demonstrating that 75% show clear signs that they are undergoing some kind of interaction. We compare these results with a control sample of quiescent early-type galaxies and find a similar rate of interaction (68%). However, we also find that the surface brightness of the features of the type II quasars are up to 2 mags brighter than those for the control sample, suggesting a difference in the types of mergers that the two groups are undergoing. We also compare our results with those for a sample of powerful radio galaxies and find very similar values for the surface brightness of the detected features.
« Newer Older »
Upcoming talks
No talks scheduled for the next days.








