Found 24 talks width keyword early universe
Abstract
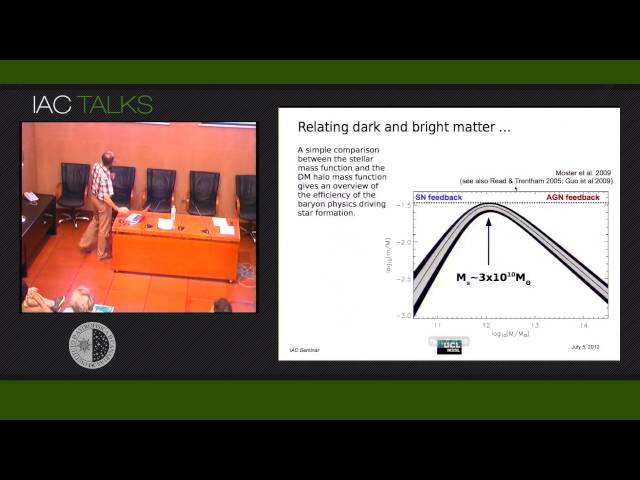
Massive early-type galaxies constitute an ideal test bed to probe our understanding of galaxy formation and evolution. Their high mass, spheroidal morphology and overly old stellar populations, along with their presence over a wide range of redshifts put to the test our current paradigm of formation via hierarchical growth. In this talk I will review recent work focused on the dark and bright sides of this problem. The former is tackled via gravitational lensing, comparing the dark matter and luminous components out to several effective radii, probing the efficiency of baryon collapse and ejection, and its feedback on the dark matter distribution (adiabatic compression). The bright side of early-type galaxies is approached via photo-spectroscopic analyses of the stellar populations, revealing a complex formation and assembly history with two well-defined phases of growth, and an intriguing connection with the "microphysics" of star formation.

Abstract
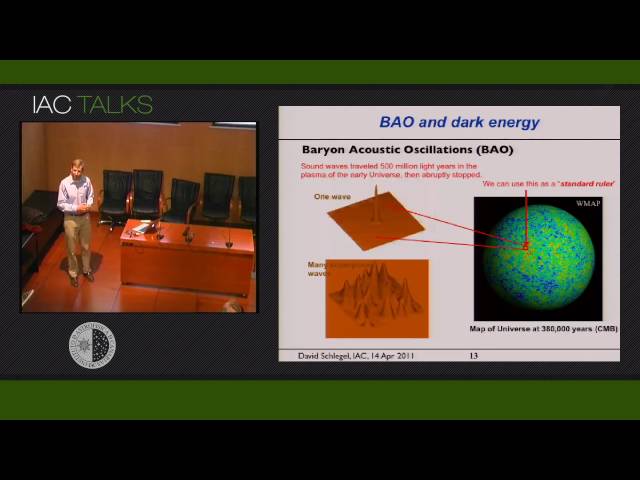
I will discuss how the acoustic oscillations that propagate in the photon-baryon fluid during the first million years of the Universe provide a robust method for measuring the cosmological distance scale. The distance that the sound can travel can be computed to high precision and creates a signature in the late-time clustering of matter that serves as a standard ruler. Galaxy clustering results from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey reveal this feature, giving a geometric distance to a redshift of 0.3 and an accurate measurement of Omega_matter. I will review our recent work on the theory and practice of the acoustic oscillation method and our latest cosmology results from SDSS-II. I will then present SDSS-III, which will use the acoustic method to produce 1% distance measurements in order to map the curvature and expansion history of the Universe and measure the evolution of dark energy.

Abstract
I will review some theoretical ideas in Cosmology different to the standard "Big Bang": the Quasi-steady State model, Plasma Cosmology model, non-cosmological redshifts, alternatives to non-baryonic dark matter and/or dark energy, and others. Some open problems of Cosmology within the standard model will also be summarized.

Abstract
Abstract
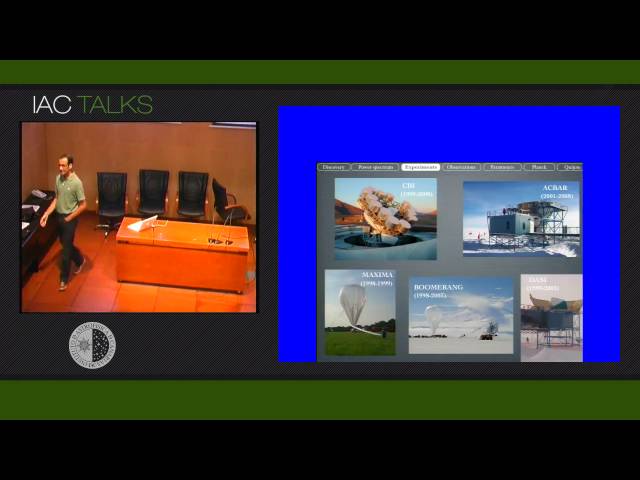
In the first part of this talk I will present a historical review of the CMB observations, one of the most powerful cosmological probes. Following the first talk of this series, where Jose Alberto described the basic parameters that define the standard cosmological model, I will here summarize the constraints to these parameters that have been derived from these observations. I will also describe the current challenges in this field, in particular the detection of the inflation's B-mode signal through CMB polarization observations, as well as the experiments that have been developed worldwide to this aim, including IAC's QUIJOTE. In the second part, I will focus on the so-called ``missing baryon problem'', i.e. the fact that the half of the expected baryon content of the local universe remains yet undetected. I will describe the theoretical studies that provide hints on where these baryons could be located, and the observational efforts that have been undertaken in this regard.

Abstract
This is the first talk of a series of four aimed to discuss about Cosmology. Here, I will review the basic concepts of the standard cosmological model, which will be further discussed in the following talks, as well as the observational evidence in support of the Lambda-CDM model. As the subject is very broad, I will focus the discussion on topics related with inflation, dark matter and dark energy. Moreover, I will mainly discuss large scale structure probes.
Abstract
The Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey (BOSS) is a Stage III dark energy experiment on the Sloan Telescope. For the five years from 2009-2014, we are mapping 1.5 million galaxies at z<0.7. A simultaneous survey of 160,000 QSOs is mapping the hydrogen gas in absorption at redshifts 2 < z < 3. BOSS will provide the definitive measurement of the low redshift (z<0.7) BAO distance scale, and it will pioneer a powerful new method of measuring BAO at high redshift. BigBOSS is a proposed Stage IV dark energy experiment that will extend this map to 20 million galaxies over 14,000 deg2 to z=1.7. I will describe this survey and its technical status.

Abstract
This lecture will address recent progress in modeling the emergence of cosmic structure at high redshifts. Also new insights gained from numerical simulations into the processes relevant for star formation are presented. Rapid magnetic field growth in galaxies and the important role of proto-stellar outflows regulating star formation up to pc scales are particularly highlighted.

Abstract
The distribution of matter in galaxies of different luminosities and Hubble types, as inferred from observations, plays an important role in cosmology, extragalactic astrophysics, astroparticle physics, as well as in a number of issues in high-energy astrophysics, galactic astronomy, star formation and evolution and general relativity. Not withstanding the general successes of the ΛCDM model in explaining the structure and evolution of the universe, there is a growing conviction that the structural properties of the dark and luminous components in galaxies hold important clues about the nature of dark matter and about the processes that are responsible for galaxy formation. This talk is part of an international initiative known as "Dark Matter Awareness Week".The overall purpose of this event is to increase the awareness of the phenomenology of the mass discrepancy phenomenon in galaxies amongst the many scientists currently working with a theoretical, observational, experimental and simulation approach on issues involving dark matter or its alternatives. The content of the talk will be at the level of a journal club talk with an important dose of review.
Abstract
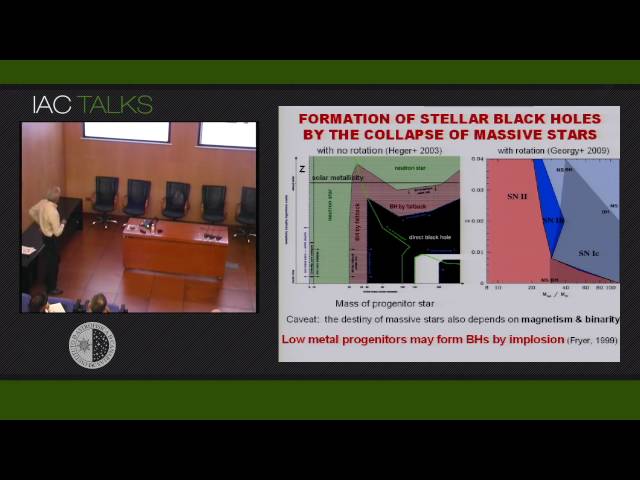
The so called "dark ages" of the universe began about 400.000 years after the Big Bang as matter cooled down and space became filled with neutral hydrogen for hundreds of millions years. How the Universe was heated and reionized during the first billion years after the Big Bang is a question of topical interest in cosmology. I will show that current theoretical models on the formation and collapse of primordial stars suggest that a large fraction of massive stars should have imploded, forming high-mass black hole X-ray binaries. Then, I will review the recent observations of compact stellar remnants in the near and distant universe that support this theoretical expectation, showing that the thermal (UV and soft X-rays) and non-thermal (hard X-rays, winds and jets) emission from a large population of stellar black holes in high mass binaries heated the intergalactic medium over large volumes of space, complementing the reionization by their stellar progenitors. Feedback from accreting stellar black holes at that epoch would have prevented the formation of the large quantities of low mass dwarf galaxies that are predicted by the cold dark matter model of the universe. A large population of black hole binaries may be important for future observations of gravitational waves as well as for the existing and future atomic hydrogen radio surveys of HI in the early universe.<< First « Newer 1 | 2 | 3 Older » Last >>
Upcoming talks
No talks scheduled for the next days.








