.
The statistical knowledge of the distribution and abundance of sodium in the mesopause on an astronomical site is crucial for the operation of Laser Guide Star Adaptive Optics systems. The first detection of mesospheric sodium with a laser on Teide Observatory took place successfully on 5th December 2001 (Fig. 1).
This achievement is within the framework of mesospheric sodium layer monitoring on Teide Observatory. The outcomes can be extended to Roque de los Muchachos Observatory because the proximity (130 km) and similar characteristics between both observatories.
A bistatic configuration system (Fig. 6), launching the sodium laser beam with the Optical Ground Station telescope (Fig. 2), permits the detection of the resonant backscattering emission by mesospheric sodium atoms. The main goal of 1m OGS telescope is the optical communications with artificial satellites. We use part of its infrastructure in the Coudè room to arrange the launching optical system (Fig. 4, 5).
.
|
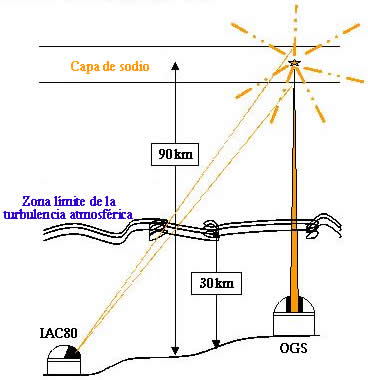 Fig.
6.- Diagram of the bistatic configuration. The sodium laser beam is launched from the OGS telescope and the resonant backscattered light from the sodium layer in the mesopause is detected with the IAC80 telescope.
Fig.
6.- Diagram of the bistatic configuration. The sodium laser beam is launched from the OGS telescope and the resonant backscattered light from the sodium layer in the mesopause is detected with the IAC80 telescope.
|
|
.
Fig. 1 shows two peaks in the emission, which points out to the presence of a sporadic layer. This phenomenon could be especially importante for the efficiency of the wavefront sensor of the Adaptive Optics systems. Variations of the sodium abundance would affect to the sentivity of the sensor, movements of the layer in hight would provoke errors in the focus of the sensor (the frequency is important), and changes of the vertical distribution (sporadic layers) would limit the performances of the sensor.
.
|
For more information, please click  in the main page in the main page
|
--0-- |
This work has been carried out by Sergio Chueca, Ángel Alonso, and Jesús J. Fuensalida (PI)
|
|
|
 ....
....  ....
....